Figure 1

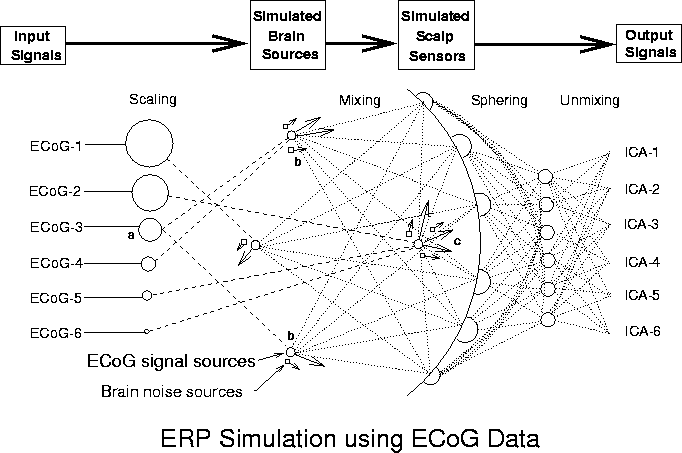
Figure 1. Schematic overview of the simulations.
Input signals (ECoG-1 to ECoG-6), minimally correlated (|r| < 0.085) 600-point data epochs taken from different times and channels in an available ECoG data set were scaled relative to one another (Scaling) and assigned to single- or multiple-dipole brain sources (longer arrows). In some conditions, one source signal (a) was projected through bilateral dipole sources (b) approximately simulating a bitemporal source in the auditory cortices. Other signals were assigned to sources modeled as single dipoles with different orientations at the same brain location. Six weak ECoG (noise) sources (shorter arrows) were positioned near the seven signal dipoles. After initial "sphering" of the simulated ERP data, source separation was performed via the "unmixing" matrix produced by the ICA algorithm. Spatial filtering of the sphered simulated ERP data by multiplying with the unmixing matrix produced output component activation waveforms (ICA-1 to ICA-6).